1. What is electricity?
Answer:The phenomenon of existence and change of electric charge. Electricity is an important energy source.
2. What is the electric field?
Answer: the formation of the field around the charged body, can transfer the interaction between the charged body.
3. What is meant by electric charge?
A: The positive or negative charge of an object or a point of mass that constitutes an object.
4. What is meant by potential?
A: unit positive charge at a point with the energy, called the point of potential.
5. What is called voltage and its basic unit and common unit is what?
Answer: The potential difference between two points in a circuit is called voltage. Its basic unit is the volt. Abbreviated volts, symbol v, commonly used units of kilovolts (kv), millivolts (mv).
6. What is the current?
Answer: The directional motion of electric charge under the action of electric field force is called current.
7. what is called resistance? What are its basic and common units?
Answer: When the current flows in a conductor, it is subject to a certain resistance, and this resistance is called the resistance of the conductor. Its basic unit is the ohm, referred to as ohm, the symbol for Ω, commonly used units are kilo-ohm (kΩ), megohm (mΩ)
8. What is a conductor insulator and semiconductor?
Answer: It is easy to conduct current objects called conductors. In the normal state almost can not conduct current objects called insulators. Conductivity between the conductor and insulator objects called semiconductors.
9. What is called capacitance, its basic units and common units is what?
Answer: Capacitor at a certain voltage to store the size of the charge capacity is called capacitance. Its basic unit is farad, the symbol for F, commonly used symbols and microfarad (MF), micro microfarad (PF), 1F = 106MF = 1012MMf (PF).
10. What is called capacitor?
Answer: A circuit element that stores charge and electrical energy (potential energy) in a container.

11. What is the inductance of its basic units and common units?
A: The ability of a coil to generate a self-induced electric potential by passing a certain amount of varying current is called the inductance of the coil. It is called inductance for short. Its common unit is the millilitre, symbolised as H, and the common unit is the millihenry (MH). 1H=103MH
12. What is the role of inductance?
Answer: Inductance in the DC circuit does not play a role, on the sudden change of loads and AC circuits play a role in resisting changes in current.
13. what is capacitive reactance what is inductive reactance what is reactance what is impedance what is their basic unit?
Answer: The capacitance in the circuit of the alternating current in the hindering effect is called capacitive resistance.
Inductance in the circuit of alternating current play a role in the obstruction is called inductive reactance.
The total effect of capacitance and inductance on the alternating current in a circuit is called reactance.
Resistance, capacitance and inductance in a circuit to the alternating current caused by the hindering effect of impedance.
Their basic unit is the ohm (Ω).
14. What is meant by circuit?
Answer: The path of current through an electrical device. Circuit usually consists of four parts: power supply, switch, load and direct wire.
15. What is meant by DC and AC circuits?
Answer: A circuit containing a DC power source is called a DC circuit.
Circuits containing an AC power source are called AC circuits.
16. What is meant by circuit diagram?
Answer: A diagram that shows the current path of the various components, devices, devices. Or with the state-specified text and
17. What is a power plant?
A: It is a plant that converts various primary energy sources contained in nature into electricity (secondary energy).
18. What are the types of power plants?
A: Thermal power plants; hydroelectric power plants; thermal power plants; nuclear power plants; wind power plants; solar power plants, etc.
19. What is the composition of the power system?
A: It consists of generators, transformers, power lines and power equipment.
20. What is an electricity network?
A: It is a network that connects transmission lines of various voltage levels and various types of substations.

21. What are the types of substations and distribution centres?
A: There are outdoor substations, indoor substations, underground substations, mobile substations, box-type substations, outdoor simple substations.
22. What is the task of the distribution house?
A: It is to receive electric energy and distribute electric energy.
23. What is the task of the substation?
A: is to receive power, transform voltage and distribution of power.
24. What is the role of power lines?
A: transport and distribution of electrical energy.
25. What are the components of overhead lines?
A: Mainly including towers, insulators, wires, cross-arms, fittings, grounding devices and foundations.
26. What are the types of towers?
A: Usually there are cement poles, metal poles (pylons, steel poles, steel poles, etc.).
27. What are the types of insulators?
A: Needle, butterfly, suspension and porcelain cross-arm type.
28. What are the three main types of wire?
A: single-stranded wire, multi-stranded wire, composite multi-stranded wire.
29. The material and structure of the conductor, said how?
A: L aluminum conductor; T copper conductor; G steel conductor; LG steel core aluminum conductor; J multi-stranded stranded wire; TMY copper bus; LMY aluminium bus.
30. What are the common electrical equipment for overhead lines?
A: A. falling fuse; B. isolation switch; C. high-voltage column switch (load switch); D. lightning arrester; E. column power container, etc..

31. What is a high-voltage line?
A. Overhead lines or cable lines that are responsible for the transmission and distribution of electrical energy, with a voltage of 3~35KV and above.
32. What is the low-voltage line?
A: The role of overhead lines or cable lines responsible for the distribution of electrical energy, the voltage of 1KV or less power lines. Typical 220V/380V power lines.
33. What is the role of the power supply bureau?
A: The power grid to implement power management, distribution, maintenance and technical support.
34. What is the power distribution room?
A: It is a place for centralised control of high and low-voltage complete sets of devices, acceptance and distribution of electric energy.
35. What is the role of high-voltage appliances in the power system?
A: In the process of electric energy production, transmission and distribution, it plays the role of control, protection and measurement.
36. What is a high-voltage device?
A: It is a switch-based set of electrical appliances, which is used in the power distribution system, for the acceptance and distribution of electrical energy. Control, measurement, protection and adjustment of the line.
37 What is a low-voltage appliances?
A: It is used for the rated voltage of 1000V AC or 1500V DC and below, and plays the role of protection, control, regulation, conversion and switching appliances in the circuit composed of power supply system and electrical equipment. 38.
38 What is a low-voltage complete set?
A: Low-voltage switching appliances and control appliances composed of complete sets of equipment. 39.
39 low-voltage complete sets of equipment, including which two types?
A: electrical control equipment; power distribution equipment (or power distribution) two types.
40. What is electrical control equipment? What is its use?
A: refers to a variety of production machinery, power transmission control equipment, its direct control of the object is mostly electric motors. Mainly used in metallurgy, mining, locomotives, ships, various production machinery and lifting and transport machinery.

41 What is the power distribution equipment?
A: refers to a variety of power plants, substations and factories and mines in the low-voltage distribution system for power, power distribution and lighting equipment.
42. substation power outage operation steps are?
A: Disconnect the power supply, check the power, install temporary grounding wire, hanging signs and installing the fence.
43. What are the main high-voltage primary equipment?
A: Mainly high-voltage fuse; high-voltage disconnect switch; high-voltage load switch; high-voltage circuit breaker.
44. What is the main function of high-voltage fuse?
A: When the passing current exceeds the specified value of the melt and break the circuit protection appliances. Its function is mainly to protect the circuit and the equipment in the circuit for short-circuit protection.
45. What is the main function of high-voltage disconnecting switch?
A: It is mainly to isolate the high-voltage power supply to ensure the safe maintenance of other electrical equipment (including lines). Because there is no special arc extinguishing structure, it can not cut off the load current and short-circuit current.
46. What is the main function of high-voltage load switch?
A: with a simple arc extinguishing device, and thus can through a certain load and overload current function, but can not break the short-circuit current, but also has the isolation of high-voltage power supply, to ensure the safety of the function.
47 What is the main function of high-voltage circuit breaker?
A: The main function is, not only can pass the normal load current, but also can connect and withstand a certain period of short-circuit current, and can be automatically tripped under the action of the protective device to remove the short-circuit fault.
48. What are the main low-voltage primary equipment?
A: Mainly low voltage fuse; low voltage knife switch; low voltage knife fuse switch and load switch; low voltage circuit breaker.
49. What is the main function of low voltage fuse?
A: It mainly realises the short-circuit protection of low-voltage distribution system, and some of them can also realise its overload protection.
50. What is the main function of low-voltage knife switch?
A: No-load operation, used as disconnecting switch.
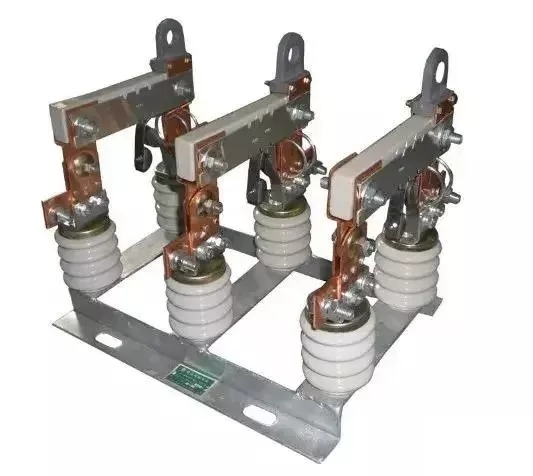

51. What are the main functions of low voltage knife-fused switches and load switches?
A: Low-voltage knife-fused switches have the dual functions of knife switches and fuses. The main function of the load switch is to effectively switch off the load current and provide short-circuit protection.
52. What is the main function of low-voltage circuit breaker?
A: It can not only pass the circuit with load, but also trip the circuit automatically in short circuit, overload and loss of voltage.
53. What is a DC motor?
A: The rotating motor whose output or input is DC electrical energy is called DC motor.
54. DC motor used in which places?
A: For large steel rolling equipment, large precision machine tools, mine winches, trams and other places.
55. What is the basic structure of DC motor?
A: It is mainly composed of two parts: stator and rotor.
56. What are the two types of DC motor excitation?
A: There are two types: he-excited and self-excited.
57. What is an asynchronous motor?
A: Also known as induction motor, is the air gap rotating magnetic field and rotor winding induction current interaction to produce electromagnetic torque, so as to achieve electromechanical energy conversion of a kind of AC motor.
58. What are the two forms of asynchronous motors according to the rotor structure?
A: squirrel cage, winding asynchronous motor.
59. What is the basic structure of asynchronous motor?
A: It is composed of two basic parts, the stationary part is called stator and the rotating part is called rotor. There is a certain air gap between the stator and the rotor.
60. What are the two types of connections for asynchronous motors?
A: There are star (Y) connection and triangle (△) connection.

61. What are the general protections for small and medium capacity asynchronous motors?
A: A. Short-circuit protection: Generally, fuses are used as short-circuit protection devices; B. Loss-of-voltage protection: The electromagnetic coil of the magnetic starter plays the role of loss-of-voltage protection in the control circuit of the starter motor. Automatic air switches, autocoupler voltage reduction compensators are generally equipped with a loss of voltage release device, C. Overload protection: generally use a thermal relay as the motor’s overload protection device.
62 A three-phase asynchronous motor, its nameplate indicates the rated voltage of 220/380 V, should be how to connect?
A: When the power line voltage is 220V, use the triangle (△) connection method
A: When the power line voltage is 220V, the star (Y) connection is used.
63. What is soft start of motor?
A: The input voltage of the motor rises gradually from zero with a preset function until the end of starting, and the motor is given full voltage, which is called soft starting. During the soft starting process, the motor starting torque increases gradually, and the speed increases gradually.
64. What kinds of starting methods are available for soft starting?
A: (1) Ramp up soft start.
(2) Ramp constant current soft start.
(3) Step starting.
(4) Pulse impact starting.
65. What is a soft starter?
A: Soft starter is a new equipment for controlling squirrel cage asynchronous motor, which is a novel motor control device integrating soft starting, soft stopping, light-load energy saving and various protection functions.
66. What is the application range of soft starter?
A: In principle, cage-type asynchronous motors can be used in all kinds of applications that do not require speed regulation. The current scope of application is AC 380V (can also be 660V), motor power from a few kilowatts to 800kW. soft starter is particularly suitable for a variety of pump loads or fan loads, the need for soft starting and soft stopping occasions.
67. What is the difference between soft start and traditional reduced voltage starting method?
Answer: (1) No inrush current. When starting the motor, the soft starter makes the motor starting current rise linearly from zero to the set value. There is no impact on the motor, which improves the reliability of power supply, smooth starting, reduces the impact torque on the load machinery and prolongs the service life of the machine.
(2) There is a soft stop function, that is, smooth deceleration and gradual shutdown, which can overcome the shortcomings of instantaneous power failure and shutdown, reduce the impact on the heavy machinery, avoid the water hammer effect of the high range water supply system, and reduce the damage to the equipment.
(3) The starting parameters are adjustable, selected according to the load conditions and the relay protection characteristics of the power grid, and can be freely adjusted steplessly to the best starting current.
68. What is a frequency converter?
A: the voltage and frequency of a fixed AC power to a voltage or frequency variable AC power device called “frequency converter”.
69. What is the main difference between a soft starter and a frequency converter?
A: Frequency converter is used in places where speed regulation is required, and its output not only changes the voltage but also changes the frequency at the same time; soft starter is actually a voltage regulator, which is used for motor starting, and its output only changes the voltage and does not change the frequency. Frequency converter has all the functions of soft starter, but its price is much more expensive than soft starter, the structure is also much more complex.
70. What is a transformer?
A: is used to change the size of the AC voltage electrical equipment. According to the principle of electromagnetic induction, a certain level of AC voltage into another level of AC voltage to meet the needs of different loads.

71. What are the classifications of transformers?
A: Transformers are divided into power transformers and special transformers. Power transformers are divided into oil-immersed and dry type. At present, oil-immersed transformers are used as step-up transformers, step-down transformers, contact transformers, and distribution transformers, dry-type transformers are only used in some distribution transformers.
72. transformer is composed of which parts?
A: generally by the core, winding, tank, insulation casing and cooling system and other five main parts.
73. transformer in operation, what are the losses?
A: copper consumption, iron consumption.
74. transformer tap why can play a regulatory role?
A: The voltage of the power system is with the operation mode and the size of the load changes, the voltage is too high or too low, will affect the service life of the equipment. Therefore, in order to ensure the quality of power supply, it must be adjusted according to the change of system voltage. Changing the tap is to change the number of turns of the coil, that is, to change the transformer changes, but also changes the voltage, so play a role in regulating the voltage.
75. What kinds of power cables are commonly used?
A: oil-paper insulated cables, plastic insulated cables (PVC insulated cables, polyethylene insulated cables), cross-linked polyethylene insulated cables, rubber insulated cables and so on.
76. 3 ~ 10KV high-voltage power lines are generally equipped with what protective devices?
A: 3 ~ 10KV power distribution substation common relay protection device overcurrent protection, current protection, transformer gas protection and low voltage protection.
77. What is the substation (station) of the operating power?
A: substation (station) switching control, relay protection, automatic devices and signalling equipment used by the power supply is called the operating power supply.
78. What are the two types of operating power?
A: AC and DC operating power.
79. What types of relays are commonly used according to the principle of action?
A: Electromagnetic, inductive, electric, magnetoelectric.
80. What lightning protection equipment is usually used for overvoltage protection?
A: There are lightning rods, lightning wires, and lightning arresters.

81. What is electrical instrumentation?
A: Electrical instrumentation is to achieve the electromagnetic measurement process required in the general term of the technical tools.
82. What are the classification of commonly used electrical instrumentation?
A: Indicating instruments, comparative instruments, digital instruments and circuit detection devices, recording instruments and oscilloscopes, extended range devices and converters.
83. What is electrical safety equipment?
A: It is used to protect the safe operation of electrical work and personal safety of indispensable tools and appliances, etc., they can prevent electric shock, arc burns and falls and other injuries occurring.
84. What are the electrical safety appliances?
A: insulated safety equipment (insulated boots, insulated gloves, insulated operating rod, insulated pliers), electrical detectors, sudden incoming protective gear, temporary earth wire, signage, work-at-height safety equipment (boards, foot buckles) and other safety gear.
85. What are the components of an automatic control system?
A: Generally by the input link, amplification link, implementation link, feedback link and comparison link and so on. 86.
86. What are the causes of short-circuit?
A: The causes of short-circuit: (1) wiring errors; (2) insulation damage; (3) operating errors; (4) mechanical damage.
87. What are the hazards of a short circuit?
A: Because the short circuit current does not pass through the load, only in the power supply internal flow, the internal resistance is very small, so that the current is very large, strong current will produce a large thermal and mechanical effects, may cause damage to the power supply or circuit, or cause a fire.
88. Can a short circuit be used in production?
A: welding machine using a short circuit to generate high current in the welding rod and workpiece arc welding; motor start current is very large, can be connected in parallel on the ammeter switch off, the meter short circuit, motor starting current does not pass through the ammeter, the meter to play a protective role in the start is completed will be disconnected from the switch.
89. What is the electrical gap?
A: electrical appliances with potential difference between two adjacent conductors, the shortest distance through the air
90. What is creepage distance?
A: electrical appliances with potential difference between two adjacent conductive parts, the shortest distance along the surface of the insulator.
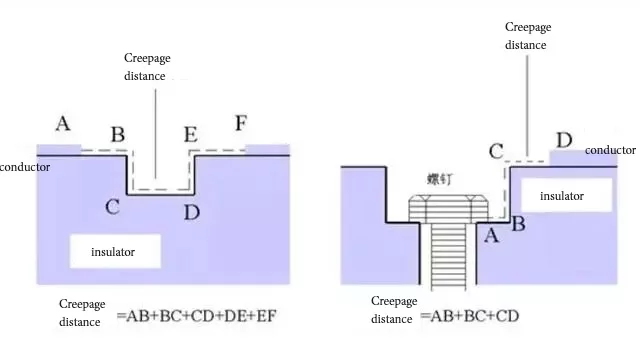
91. What is the creepage ratio distance
A: creepage distance and the ratio of the working voltage, the unit is m/kv.
92. What is the rated operating voltage?
A: In the specified conditions, to ensure the normal operation of the electrical voltage value.
93. What is the rated insulation voltage?
A: Under the specified conditions, used to measure the electrical appliances and their components of different potential part of the insulation strength, electrical clearance and creepage distance of the nominal voltage value.
94. What is the rated operating current?
A: Under the specified conditions, to ensure the normal operation of the current value of the appliance.
95. What is the rated heating current?
A: In the specified conditions of the test, electrical appliances in 8h under the working system, the temperature rise of the components does not exceed the limit value of the maximum current can carry.
96. electrical test is divided into two categories?
A: insulation test and characteristic test two categories.
97. What are the main components of power drag?
A: electric power drag is composed of four basic parts of the motor, transmission, control equipment and production machinery.
98. What is the three-phase symmetrical winding?
A: It refers to the phase winding structure parameters are the same, and in the space of each other 120 ° phase difference between the three-phase winding.
99. What is the function of circuit breaker interrupter cover?
A: (1) guide the arc to blow out longitudinally, thus preventing the occurrence of phase-to-phase short circuit; (2) make the arc contact with the insulating wall of the arc extinguishing chamber, thus cooling rapidly, increasing the de-stressing effect, increasing the pressure drop of the arc column, and forcing the arc to be extinguished.
100. Why use shunt compensation capacitors in industrial and mining enterprises?
A: Shunt compensation capacitors to compensate for the reactive power required by the inductive load of the power system to: (1) improve the voltage quality of the grid.
(2) Improve power factor.
(3) Reduce line losses.
(4) Improve the output of transformers and lines.

